The world of wireless communication is growing rapidly, and at the head of this change is 5G technology – the fifth generation of mobile networks that promise to redefine connection. But what is 5G technology and how does it work? Simply put, 5G is designed to be more reliable and capable of 5G at the same time to connect to a large number of equipment. It refers to the previous generations as 4G but introduces a series of innovations that meet future digital requirements.
Unlike previous networks, which mainly focus on improvement in internet speed, 5G has advanced technologies such as millimeter waves, large-scale MIMO (multiple inputs with multiple outputs), and network slices to provide ultra-lo-loop and incredibly high data thrown to provide high data throws. It allows applications that were once science fiction – such as autonomous cars, smart cities, and distance operations – to become a reality. This article dives deep into 5G technology features, function, and significance, and depicts an image of its influence in industries and countries, including a closer look at 5G technology in Pakistan.
Table of Contents
Understanding 5G Technology: The Foundation of Next-Gen Connectivity
To truly grasp why 5G technology matters, we must first explore the core principles behind it and what sets it apart from previous generations.
What Makes 5G Different? A Technical Overview
5G wireless technology operates on a suite of innovations that optimize the way data travels through networks. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
- MMWAVE: Unlike 4G, which uses frequencies below 6 GHz, 5G can use high existing bands (24 GHz and above). These millimeters the waves can carry large amounts of data, but a dense network of small cells is needed.
- Large -scale MIMO: This technique at the same time involves the capacity and efficiency of base stations with dozens of or hundreds of antennas to operate many users.
- Beamforming: By focusing on wireless signals directly on devices instead of wide broadcast, the beam liner increases the quality of the signal and reduces the intervention.
- Network disc: 5G operators, from games to emergency services, allow the virtual “slices” of the network that fits specific applications, optimizes the performance based on the requirement.
- Edge Computing: By processing the data near the user, 5G reduces delay, enabling real -time applications that improved reality and remote control of the machinery.
Key Features of 5G Technology That Will Transform Our World
Understanding the features of 5G technology helps illustrate why it is so crucial for the next era of digital innovation.
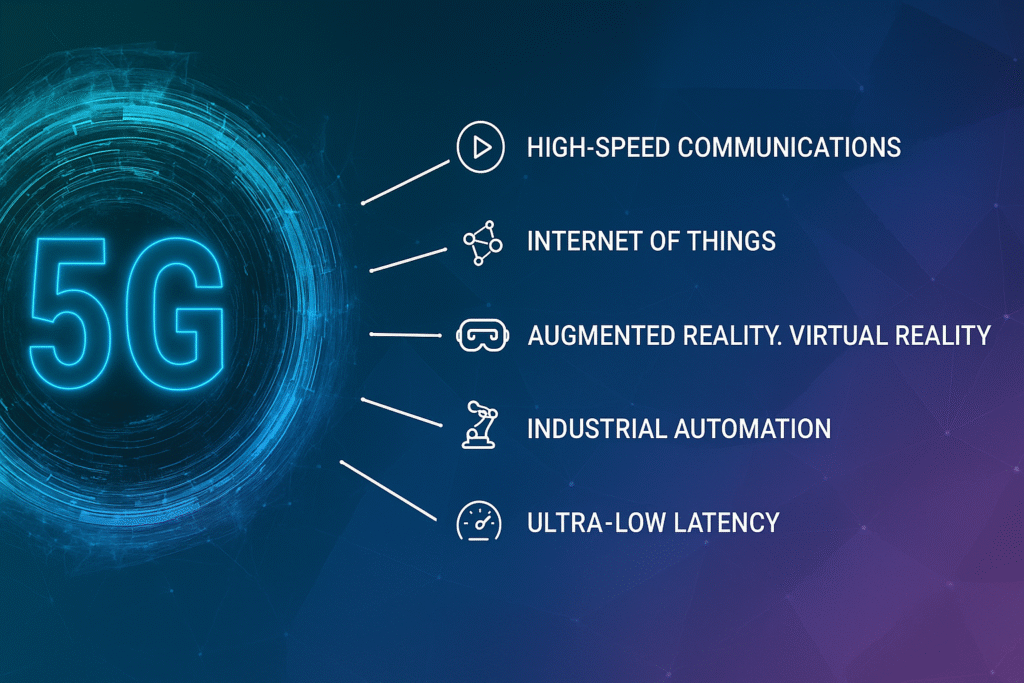
Speed and Bandwidth: Breaking Speed Limits
5G offers data rates up to 10 Gbps, enabling ultra-fast downloads and seamless streaming of 4K or even 8K video content. This unprecedented bandwidth supports not just consumer applications but also critical enterprise solutions.
Ultra-Low Latency: Near-Instantaneous Response
Latency is the delay before data begins to transfer after an instruction. 5G drastically cuts latency to around 1 millisecond, compared to about 30-50 milliseconds on 4G, which is essential for applications requiring real-time feedback like remote surgeries and driverless cars.
Massive Connectivity: Supporting the Internet of Things (IoT)
With the expected explosion of connected devices—ranging from smart home sensors to industrial robots—5G is designed to handle up to a million devices per square kilometer, far surpassing the capabilities of 4G.
Enhanced Reliability and Security
5G networks promise higher reliability and better security protocols, making them suitable for mission-critical applications, including emergency communications and financial transactions.
The Importance and Benefits of 5G Technology in Today’s Digital Age
Why do we need 5G technology? Beyond just speed, the benefits it offers are profound and far-reaching.
Economic Growth and Innovation
The adoption of technology is projected to generate trillions of dollars globally by enabling new services and industries, such as smart manufacturing, telemedicine, and immersive entertainment.
Enabling Smart Cities and Infrastructure
5G’s high capacity and low latency make it ideal for managing smart grids, traffic systems, and public safety networks, improving urban life and resource efficiency.

Revolutionizing Healthcare
From remote diagnostics to robotic-assisted surgeries, 5G supports the digital transformation of healthcare by enabling high-quality video streaming and real-time data exchange.
Boosting Education and Remote Work
With 5G, virtual classrooms and remote work platforms become more immersive and efficient, bridging gaps caused by geography and infrastructure limitations.
How Does 5G Work on a Technical Level?
To appreciate the mechanisms behind 5G, it’s important to understand the technologies that power it.
Radio Access Network (RAN) Evolution
5G introduces a new radio interface known as New Radio (NR), which operates on various frequency bands, including sub-6 GHz and mmWave. This allows networks to optimize coverage and capacity.
Core Network Upgrade
Unlike previous generations, 5G’s core network is designed to be fully cloud-native, flexible, and software-defined, allowing dynamic resource allocation and network slicing.
Role of Small Cells and Infrastructure
Due to the higher frequencies used, 5G networks require many small, low-power cells close to users, integrated into street lamps, buildings, and other urban infrastructure to ensure seamless coverage.
Which Countries Are Leading the 5G Revolution?
As 5G rolls out worldwide, different countries have taken unique approaches toward adoption, infrastructure investment, and regulation.
Global Leaders in 5G Deployment
Countries like South Korea, the United States, China, and parts of Europe have aggressively deployed 5G networks. South Korea, for example, was among the first to launch nationwide 5G, boasting rapid consumer adoption.
Which Countries Have Banned 5G ?
Concerns over security and health have led some countries to delay or ban certain 5G infrastructure providers. For instance, some Western countries have restricted equipment from specific manufacturers citing national security risks.
5G Technology in Pakistan: Progress and Challenges
Pakistan is gradually embracing 5G technology, with trials underway and regulatory frameworks evolving. Challenges include infrastructure costs and ensuring equitable access, but the country’s youth-driven digital economy stands to benefit significantly.
Addressing Common Concerns: Is 5G Harmful to Humans?
One of the frequently asked questions is about the safety of 5G technology.
Understanding the Science Behind 5G and Health
The radio frequencies used by 5G fall within the non-ionizing spectrum, meaning they do not have enough energy to damage DNA or cells. Studies by global health organizations, including the WHO, have found no conclusive evidence linking 5G to adverse health effects.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About 5G Technology
What is 5G technology and how does it work?
5G technology is the fifth generation of wireless communication networks that use advanced radio frequencies, new infrastructure, and network designs to provide ultra-fast internet speeds, low latency, and support for massive connectivity.
What are the features of 5G technology?
Key features include higher speeds (up to 10 Gbps), ultra-low latency (1 ms), massive device connectivity, improved reliability, and enhanced security.
How does 5G technology work on which technology?
5G works on a combination of millimeter wave frequencies, massive MIMO antennas, beamforming, network slicing, and a cloud-native core network to optimize performance.
What are the benefits of 5G technology?
Benefits range from faster internet and real-time communication to enabling smart cities, remote healthcare, IoT expansion, and economic growth.
Why do we need 5G technology?
We need 5G to support the increasing demand for high-speed, low-latency connections and the growing number of connected devices powering future technologies.
Which countries are using 5G technology?
Leading countries include South Korea, the USA, China, Japan, and several European nations, with many others, including Pakistan, beginning rollout phases.
Is 5G technology harmful to humans?
Current scientific consensus states that 5G is safe as it uses non-ionizing radiation, but ongoing studies continue to monitor long-term effects.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of 5G technology?
Advantages: ultra-fast speeds, low latency, massive connectivity, and support for advanced applications.
Disadvantages: high infrastructure costs, shorter range of high-frequency signals, and potential cybersecurity risks.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future with 5G Technology
The arrival of 5G technology is an important moment in the development of wireless communication. This not only promises outstanding speed and connection but also performs ground tasks for innovations that can change industries, economies, and everyday life around the world. From enabling smart cities to revolutionizing the health care system, the importance of 5G technology cannot be eliminated.
As investment in countries around the world adapts to 5G, the entire technology capacity is felt. This revolution is not just about sharp phones – it’s about creating a connected ecosystem in which we live, work, and interact.
For Pakistan and many other developing countries, Hugging 5G represents the opportunity to jump into a digital future, progress globally, and drive innovation. The question is no longer whether 5G will change the world, but how soon and to what extent.
The 5G time is here – are we ready to exploit their power?



